Biophysical Profile OBS501
Biophysical Profile Transcript
Biophysical Profile
This is Dr. Cal Shipley with a review of the biophysical profile, or BPP for short.
Biophysical Profile Defintition
The biophysical profile is a noninvasive procedure for assessing fetal wellbeing. Ultrasound is used to assess for individual fetal parameters, breathing, amniotic fluid volume, fetal movement, and fetal muscle tone.
Each of these parameters is assigned a score of either zero or two, with two indicating a normal assessment. The overall BPP score is simply the sum of the scores of each of the four individual parameters. Therefore, eight is a perfect score.
The biophysical profile is sometimes performed in conjunction with a nonstress test. I’ll discuss the non-stress test a little bit later in this review.
Physiological Basis for the Biophysical Profile
The physiology that underlies the usefulness of the biophysical profile is fairly straightforward. Each of the four biophysical profile parameters are controlled by specific areas in the brain. Loss of normal biophysical profile activities may indicate suppression of brain function, either due to hypoxemia, acidemia, or ischemia.
Indications
What are the indications for performing a biophysical profile? The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends a biophysical profile be performed in any pregnancy where there is an increased risk of fetal demise during gestation. Here is a partial list of conditions in which anti-natal surveillance techniques such as the biophysical profile should be employed.
Timing and Frequency
As far as timing and frequency, the biophysical profile should be performed as soon as the increased risk of fetal demise is identified at a point during the pregnancy where delivery would be an option if the testing is abnormal. Typically, testing is performed weekly, but this frequency may be increased or decreased depending on changes in the maternal-fetal status.
Biophysical Profile Parameters
Now let’s take a closer look at each of the biophysical profile parameters starting with breathing.
Fetal Breathing
Fetal breathing is dependent on normal flow of blood and oxygen from the placenta to the respiratory centers within the brain. As with each of the four biophysical profile parameters, an ultrasound machine is to assess fetal breathing. The ultrasound transducer is applied to the mother’s abdomen in order to detect the rise and fall of the fetal chest during respiration. The breathing assessment is awarded a score of two if at least one episode of rhythmic breathing lasting at least 30 seconds is observed over a 30-minute period.
Amniotic Fluid Volume
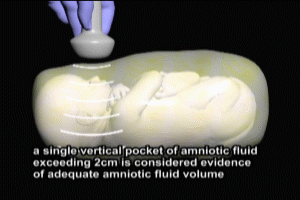
Let’s turn now to assessment of amniotic fluid volume. During the last trimester of gestation, amniotic fluid is primarily produced by the fetal kidneys, with a smaller contribution from the fetal lungs. Fluid from the kidneys flows into the amniotic sac via the fetal bladder. Normal amniotic fluid production in the third trimester is critically dependent on normal fetal kidney and placental function. When oxygen and blood flow from the placenta to the fetus are normal, the kidneys receive an appropriate portion of the blood. However, if there is impairment of flow from the placenta, the fetus selectively redistributes blood flow to the brain, heart, adrenals, and placenta and away from the kidneys and other organs. This loss of blood flow to the kidneys results in decreased amniotic fluid production.
The adequacy of amniotic fluid volume can be quite accurately determined based on ultrasound measurements of the fluid depth. A single vertical pocket of amniotic fluid, at least two centimeters in depth, is considered sufficient evidence of adequate amniotic fluid volume. With impaired placental function and subsequent reduced perfusion of blood to the kidneys, amniotic fluid volume will decrease and ultrasound will fail to detect any vertical pockets of two centimeters or greater.
Fetal Movement
The third parameter that we’re going to look at in the biophysical profile is fetal movement. Movement of the fetal musculature is dependent on adequate blood and oxygen flow from the placenta to the brain and nervous system. A score of two points is awarded if three or more discrete limb movements are detected over a 30-minute period. The three movements detected may involve three separate limbs, as noted here, or involve three discrete movements of the same limb. In addition, some authorities will accept detection of just two discrete movements over a 30-minute period as having satisfied the criteria if one of those movements is of the torso.
Fetal Muscle Tone
The fourth biophysical profile parameter assesses fetal muscle tone. Like respiration, amniotic fluid volume, and muscular movement, fetal muscle tone is dependent on an adequate supply of oxygen-rich blood from the placenta to the brain and nervous system. Points are allotted based on the detection of one or more episodes of muscle or spine extension with return to flexion over a 30-minute period. In this example, the lower arm is extended and then flexed.
Non-stress Test
In addition to assessing the four parameters that we have just discussed, many practitioners perform a non-stress test as part of the biophysical profile. Two points is awarded for a normal non-stress test. This makes a possible total of 10 points for the entire profile. Is the non-stress test an essential part of the biophysical profile? Studies have shown that when the score of the first four parameters is eight, the addition of a non-stress test does not increase the power of the profile in predicting adverse outcomes. For this reason, many practitioners perform a non-stress test only when the score of the four-part profile is less than eight. Click here to view my presentation on the Non-Stress Test.
Interpretation of the Biophysical Profile Score
Finally, let’s take a look at interpretation of the biophysical profile score.
A score of 8 out of 8 or 10 out of 10 (if the NST is included in the profile) or 8 out of 10, with two points included for amniotic fluid, is considered a normal result. The chance of fetal death within one week of the testing is very low, about 0.05%.
A score of 6 out of 10 including two points for amniotic fluid is concerning. The chance of fetal asphyxiation cannot be ruled out, and the test should be repeated in 24 hours.
A score of 6 out of 10 or 8 out of 10 when there are zero points for amniotic fluid is abnormal and carries with it a risk of fetal demise, if not delivered within one week, of approximately 10%.
A score of 4 out of 10 or less is highly abnormal and carries with it a risk of fetal demise as high as 50%. In such situations, delivery should be accomplished as soon as practicable.
Final Note
A final note. Abnormal biophysical profile scores should always be interpreted within the context of a specific maternal-fetal situation. The clinician must take into account not only the biophysical profile scores and any other antenatal testing results, but also any other risks to the fetus or the mother associated with either a delayed or forced delivery.
Cal Shipley, M.D. copyright 2020